Rare earth elements (REEs) are commonly used in consumer electronics such as televisions, cameras, and mobile phones, as well as automobile catalytic converters and rechargeable batteries due to their unique optical and magnetic properties. They are also known as the “Green Elements” because they are essential to many green energy technologies. REEs have been the subject of major media attention resulting from potential trade restrictions; this has become a particularly sensitive problem for defense organizations which rely heavily on these elements for much of their high-tech equipment.

Despite the name, these elements – defined as the 15 lanthanides plus scandium (Sc) and yttrium (Y) – are not as rare as one might think. However, due to the difficulties in extracting the metal from the ore, rare is a fitting term. From greenfield exploration, through exploratory and advanced drilling, to mine development and ore grade control, Thermo Scientific Niton x-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyzers are indispensable tools for providing you with realtime information – information that helps you make decisions in the field, without the time delays or expense of shipping samples long distances to off-site laboratories.
Application
Thermo Scientific Niton XRF analyzers are available with your choice of excitation options, providing the optimal configuration for your analytical needs.

Thermo Scientific Niton XRF analyzers deliver fast, accurate elemental analysis for intensive metals exploration and production, whether rare earth elements, base metals, or precious metals.
Our breakthrough Niton® XL3t tube-based analyzer provides an analytical range from chlorine (Cl) to uranium (U) to fill most mining needs. With its 50kV miniaturized x-ray tube, it is now possible to excite the light series of REEs (LREEs) using tube-based XRF. This includes lanthanum (La), cerium (Ce), praseodymium (Pr), and neodymium (Nd). Other elements associated with REE-bearing minerals such as thorium (Th) and Y may also be analyzed. By using the concentrations from these elements, especially Y, it is possible to infer concentrations of heavy REEs (HREEs) that are commonly associated with Y-containing host minerals. Figure 1 shows the excitation efficiency of the 50kV tube in measuring rare earth elements versus x-ray tubes with a lower voltage that are generally unsuitable for this application.
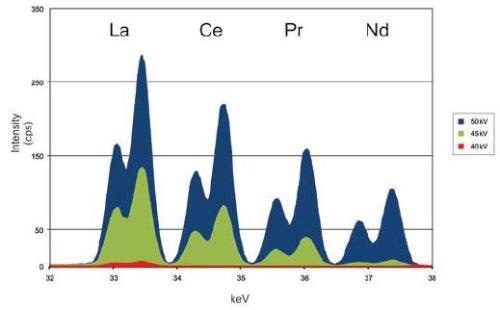
Figure 1. Comparison of excitation efficiency of various x-ray tubes for rare earth elements (REEs). Note the inability of a 40 kV x-ray tube to excite even the light REEs.
Another advantage of tube-based XRF analyzers for mineral exploration is based on their flexibility. If future targets involve other element groups, these instruments can provide reliable results with ease. These element groups can include base and ferrous metals, silver, gold pathfinders – arsenic (As), selenium (Se), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te), mercury (Hg), etc. – and platinum group metals (PGMs).
What’s more, the Niton XL3t analyzer is available with GOLDD+ technology, allowing measurement times up to 10-times faster than conventional technologies. This technology enables light element analysis, adding magnesium (Mg), aluminum (Al), silicon (Si), phosphorus (P), and sulfur (S) to help identify alteration and rock types.
Anthony N. Mariano, Ph.D., consulting exploration geologist, observes, “The [Thermo Scientific Niton XL3t x-ray tube analyzer] gives good numbers for the lights [light rare earth elements – La, Ce & Nd], as well as Y with high sensitivity. If you see Y, you have heavies [heavy rare earth elements]. It tells you if REEs are present, and if we’re enriched in the lights or the heavies.”
Our advanced isotope-based Niton XLp 522K XRF analyzers quickly analyze elements from titanium (Ti) to U. These analyzers cover a broader suite of REEs than our tube-based analyzers, and offer direct analysis of the full suite of these elements: La, Ce, Pr, Nd, samarium (Sm), europium (Eu), gadolinium (Gd), terbium (Tb), and dysprosium (Dy), as well as Y, U and Th. This breadth of elements can be vital during processing or activities other than exploration, or when direct measurement of HREEs is required.
Thermo Scientific Niton XLp 522K analyzers deliver fast analysis for an extensive list of light and heavy rare earth elements.
Depending on your need, either option, tube-based or isotope-sourced, will deliver accurate analysis; REE measurements are achieved with a minimum of sample preparation, enabling quick decisions in the field, which result in significant time and money saved.1
Additionally, both of these instruments allow straightforward trend analysis by averaging readings in real-time directly on the analyzer or by downloading results later to a PC. Once downloaded, readings may be used for report generation or post-analytical processing. They also interface with GPS devices, delivering fast, accurate, geospatially-oriented elemental analysis for intensive metals exploration and production, whether rare earth elements, base metals, or precious metals.
Method
Using the Niton XLp 522K analyzer, twenty-five certified reference materials (CRM) and lab-analyzed samples were packed into standard XRF sample cups fitted with Mylar film and measured for 150 seconds. With the Niton XL3t, seventeen CRM and lab-analyzed samples were packed into standard XRF sample cups fitted with Mylar film and measured for 120 seconds. Analysis time may vary depending on precision requirements.
Results
Figure 2. shows the correlation curves for La with comparative or certified values for both the Niton XLp 522K and the Niton XL3t.
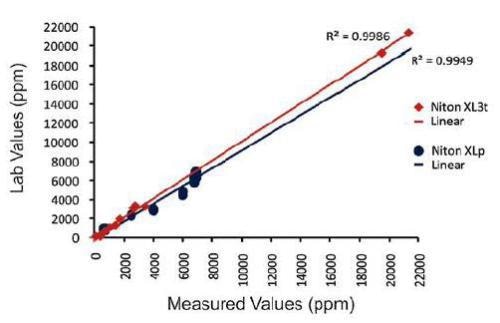
Figure 2. Niton XLp 522K and Niton XL3t correlation curve for lanthanum (La)-samples
The coefficient of determination (R2 for each element) is provided in the figures. The R2 value is a measure of how closely the data sets correlate with each other, where a perfect correlation would have an R2 of 1.
Additionally, Table 1 displays repeatability data detailing the robust precision of the Niton XLp 522K analyzer.
| Sample 43013 |
La |
Ce |
| Average |
0.623 |
1.166 |
| Standard deviation |
0.010 |
0.012 |
| % RSD |
1.6 |
1.0 |
Table 1. Repeatability data for La and Ce in sample 43013; 10 analyses were performed with the Niton XLp 522K.
Comments
The correlation coefficients and repeatability data for the key elements in REE ore analysis demonstrate the excellent accuracy and precision of both the handheld Niton XLp 522K and the Niton XL3t analyzers, indicating that they are ideal instruments for fast geochemical analysis. The instant chemistry provided allows the user to make critical decisions with a minimum of downtime, keeping projects running and productive. Additionally, the analyzers provide information that minimizes the expense and time of shipping samples off-site for analysis, both reducing costs and increasing productivity.

This information has been sourced, reviewed and adapted from materials provided by Thermo Fisher Scientific.
For more information on this source, please visit Thermo Scientific Portable Analyzers for Material ID.